Leave Your Message
-
Whatsapp
-
Whatsapp
In the construction industry, the use of **Osb Structural Beams** has gained significant attention for their versatility and strength. According to a recent report by the International Wood Products Association, the market for engineered wood products, including OSB beams, is projected to grow by 8% annually through 2027. This trend highlights the increasing adoption of **Osb Structural Beams** due to their lightweight nature and consistent quality.
James Thornton, a leading expert in sustainable construction materials, asserts, “Osb Structural Beams revolutionize modern construction by combining durability with eco-friendliness.” This sentiment reflects the growing recognition of OSB as a viable alternative to traditional timber beams. Their use can lead to reduced waste and lower carbon footprints in projects.
Despite these benefits, there are challenges that require careful consideration. Factors such as exposure to moisture can impact the longevity of **Osb Structural Beams**. Understanding these limitations is essential for optimizing their performance in various applications. As the industry evolves, continual assessment of materials like OSB becomes vital in enhancing construction practices.
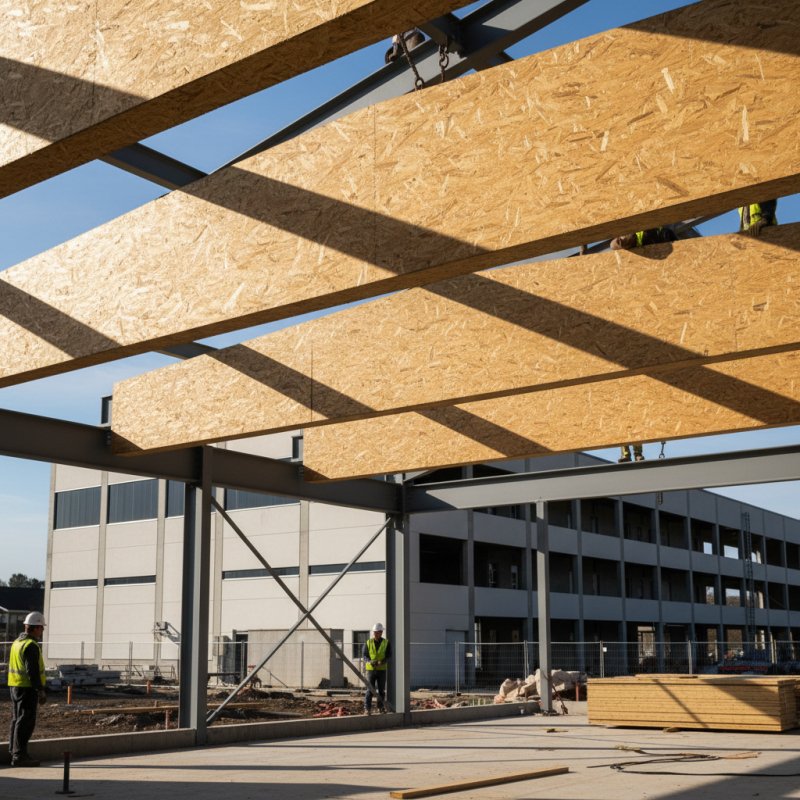

OSB (Oriented Strand Board) beams are gaining traction in construction due to their structural integrity and stability. Manufactured from strands of wood, OSB beams provide a strong alternative to traditional lumber. Their engineered nature allows for consistent performance, making them an excellent choice for various building applications. According to the APA – The Engineered Wood Association, OSB has lower moisture content and better performance under load compared to some solid wood products.
One notable benefit of OSB beams is their resistance to warping and splitting. This trait significantly enhances the overall stability of the structure. Structures using OSB beams tend to have improved long-term durability. Reports indicate that buildings with engineered wood products like OSB can experience less settling over time. This translates into fewer adjustments needed post-construction, saving time and costs.
When using OSB beams, consider the environment. They are often made from sustainably sourced materials. This makes them a greener option for builders focused on eco-friendly construction practices. Always ensure proper handling during installation. OSB can be susceptible to moisture damage if not adequately protected. Keep it covered and dry before installation.
Tip: Use OSB beams in areas where strength and stability are crucial, such as in floor joists or wall framing. Proper installation as per guidelines ensures maximum performance.

Using OSB structural beams in construction presents significant cost advantages over traditional materials. Research indicates that OSB beams can be up to 20% less expensive than conventional lumber. This reduction comes from lower production costs and faster installation times. In a competitive market, these savings can enhance a contractor's bottom line.
Moreover, OSB beams offer structural performance metrics comparable to solid wood. For instance, their strength-to-weight ratio is favorable, making them a solid choice. However, there are concerns about moisture sensitivity. Some builders have reported issues with swelling and warping if not adequately treated. This requires careful handling and design considerations.
Another aspect to consider is the sustainability of OSB. According to the Forest Products Laboratory, OSB is made from fast-growing trees that are renewable. This makes it an environmentally friendly option, yet sourcing practices can vary significantly. Ensuring that OSB is sourced responsibly is essential. While it’s cost-effective, the potential pitfalls in quality and sustainability warrant careful selection by builders. This balance of cost, performance, and environmental impact requires ongoing reflection in the construction industry.
Oriented Strand Board (OSB) has been gaining traction as a sustainable building material. It is made from small wood strands, which maximizes wood usage and minimizes waste. Reports highlight that OSB can use up to 90% of each log, whereas traditional lumber uses only about 50%. This efficient use aligns with the principles of sustainable forestry.
The production of OSB has a comparatively lower carbon footprint. According to the Forest Products Laboratory, OSB generates 50% less greenhouse gases than solid timber. This is due to the industrial process that allows for the recycling of wood waste and the use of adhesives with lower emissions. However, concerns about the formaldehyde content in some OSB products remain. Efforts to produce low-emission OSB are ongoing, but it highlights the need for continuous improvement in manufacturing practices.
OSB’s lightweight nature reduces the energy needed for transportation, thus further minimizing its environmental impact. A study by the USDA Forest Service shows that lighter materials can cut transport emissions by as much as 30%. While the benefits are notable, the industry must ensure that sourcing and production practices keep pace with sustainability goals. The journey towards fully sustainable building materials is complex, and OSB is a step, but not the final destination.
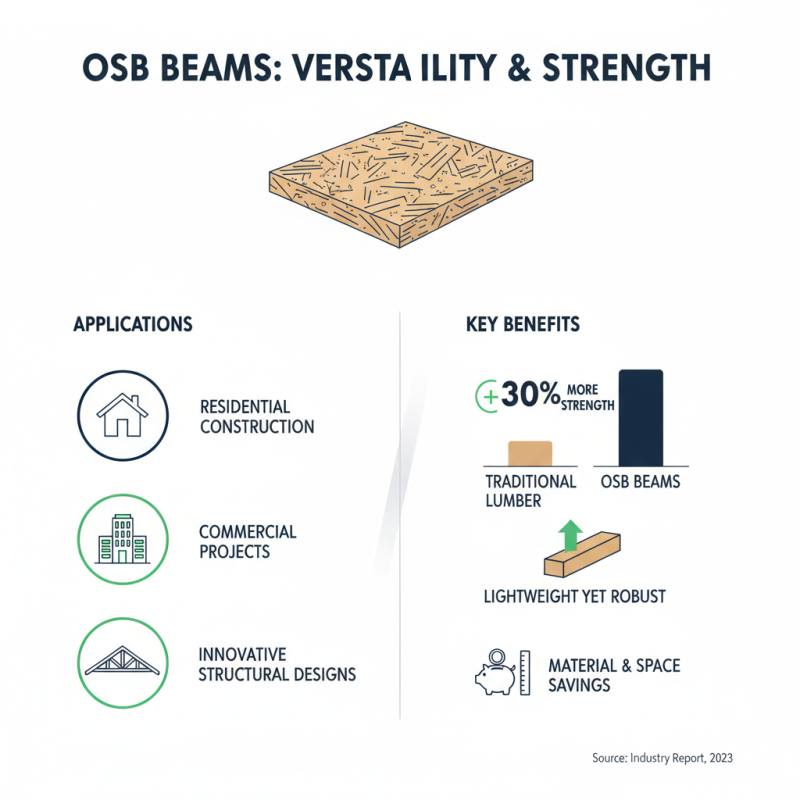
The versatility of OSB (Oriented Strand Board) beams is evident in a variety of building designs and applications. These beams are lightweight yet strong, making them ideal for both residential and commercial construction. According to a recent industry report, OSB beams can provide up to 30% more strength compared to traditional lumber per board foot. This characteristic allows for innovative structural designs that save space and material costs.
OSB beams are adaptable to numerous situations. They can be used in floor framing, wall systems, and even roofing structures. Their compatibility with modern architectural styles offers flexibility for architects and builders alike. For instance, open-concept homes benefit greatly from OSB beams, allowing larger spans that create airy spaces.
Tips: Always consider the environmental impact. OSB is often made from sustainably sourced wood. Not only does this reduce waste, but it also supports eco-friendly building initiatives.
However, it's essential to account for certain limitations. OSB beams can absorb moisture, which may affect their durability. When planning your project, be mindful of exposure to harsh weather. Proper treatment and installation can mitigate these issues. Overall, OSB beams present a practical solution with the capability to enhance diverse construction applications.
OSB structural beams offer significant ease of installation. Their lightweight nature simplifies handling on site. According to recent industry reports, the use of OSB can reduce labor costs by 30%. This efficiency can accelerate project timelines, which is crucial in construction.
Installation of OSB beams usually requires fewer tools and less time compared to traditional materials. Studies show that skilled labor can install these beams up to 20% faster. This speed does not compromise structural integrity. Construction professionals often appreciate this balance.
However, the reliance on OSB may lead to concerns about long-term durability. Some builders question moisture resistance in varied climates. It's important to address these potential pitfalls. Ensuring proper sealing and treatment can mitigate these risks and enhance performance. As builders continue to innovate, OSB’s role could evolve, shaping future practices in construction.
| Benefit | Description | Impact on Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Installation | OSB beams are lightweight, making them easier to handle and install. | Reduces labor time and improves project timelines. |
| Cost-Effective | Lower material costs compared to traditional lumber. | Helps stay within budget for construction projects. |
| Sustainability | Made from recycled wood materials, reducing waste. | Contributes to environmentally-friendly building practices. |
| Durability | Resistant to warping and splitting compared to wood. | Increases the longevity of the structural elements. |
| Design Flexibility | Can be used in various architectural designs. | Enhances design possibilities for architects and builders. |
| Thermal Performance | Provides excellent insulation properties. | Improves energy efficiency of buildings. |
| Consistency | Manufactured for uniformity and strength. | Ensures stable construction quality. |
| Resistance to Pests | Less attractive to pests compared to solid wood. | Reduces maintenance and repair issues. |
| Fire Resistance | Some OSB products offer enhanced fire resistance features. | Increases safety standards for buildings. |
| Lightweight | Significantly lighter than traditional beams. | Easier transportation and handling on-site. |